Workspaces and Pages
BlockSuite is centered around the concept of blocks. However, to handle a large number of blocks efficiently, the blocks are organized into workspaces and pages. Workspace is the highest-level container that can hold multiple pages. Page is the sub-container for organizing blocks, and each page contains a strongly typed block tree.
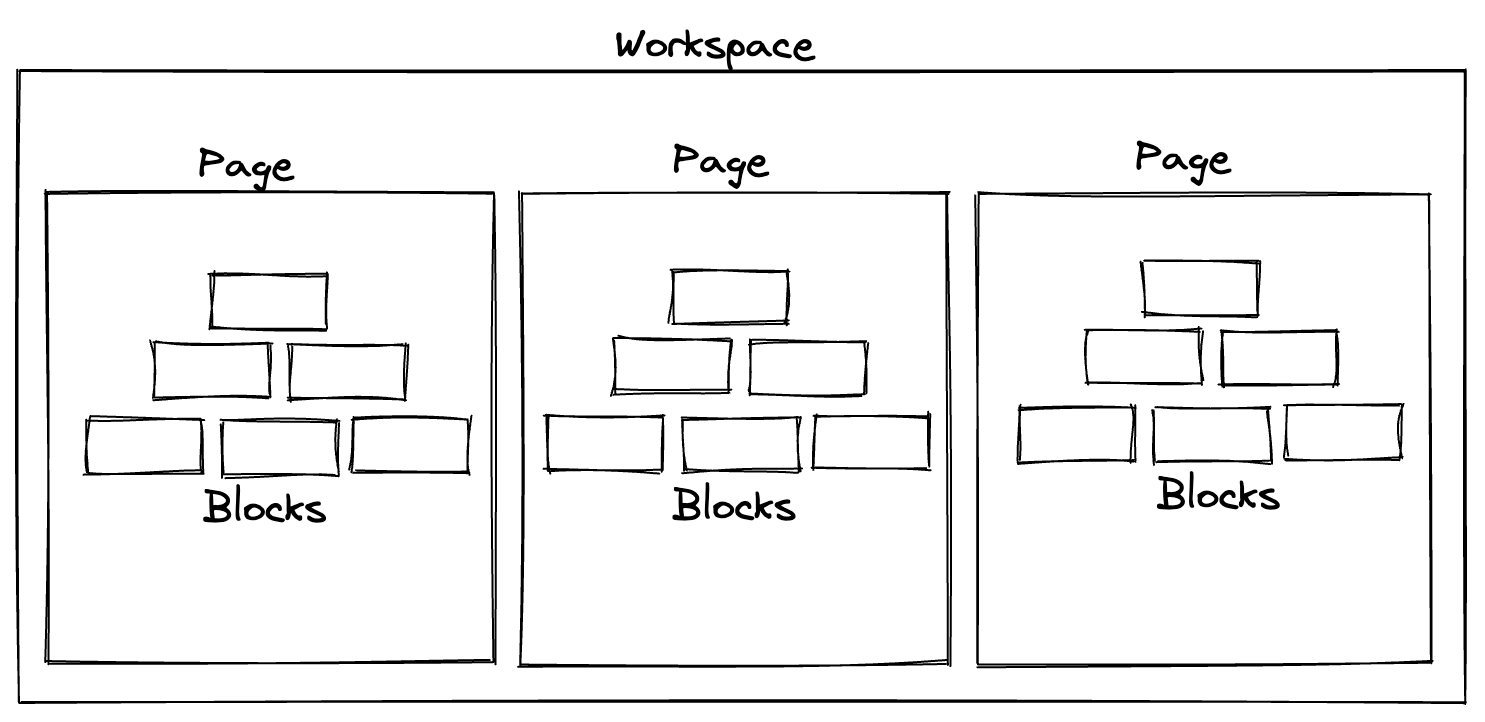
Workspaces
A workspace in BlockSuite acts as a top-level container for organizing pages. By creating workspaces, users can group and categorize different sets of pages, each representing a specific project or a collection of related content. Here is how we create a new workspace:
import { Workspace, Schema } from '@blocksuite/store';
const schema = new Schema();
// We can register a batch of blocks to the workspace
schema.register(AffineSchemas);
const workspace = new Workspace({ id: 'foo', schema });import { Workspace, Schema } from '@blocksuite/store';
const schema = new Schema();
// We can register a batch of blocks to the workspace
schema.register(AffineSchemas);
const workspace = new Workspace({ id: 'foo', schema });Pages
A page in BlockSuite serves as the actual container for organizing blocks, allowing users to operate on the block tree through its APIs. By taking the advantage of subdocuments, the page content can also be loaded asynchronously on-demand. In typical scenarios involving rich text documents, one document is represented by a single page within a workspace.
Here is how we create a new page with id page0 within the workspace:
const page = workspace.createPage({ id: 'page0' });const page = workspace.createPage({ id: 'page0' });The page instance provides a set of core APIs for performing block operations, e.g., page.addBlock, page.updateBlock, and page.deleteBlock. These APIs will be further introduced in the following sections of the document.
TIP
Block operations APIs are only available after the page is loaded. Remember to add await page.waitForLoaded() before calling these APIs.